According to different experimental test requirements, the in-situ Raman spectroscopy electrochemical cell is divided into four types:
Single cell body with single light window type
Single cell body with double light window type
H type double cell body with single side light window type
H type double cell body with double side light window type
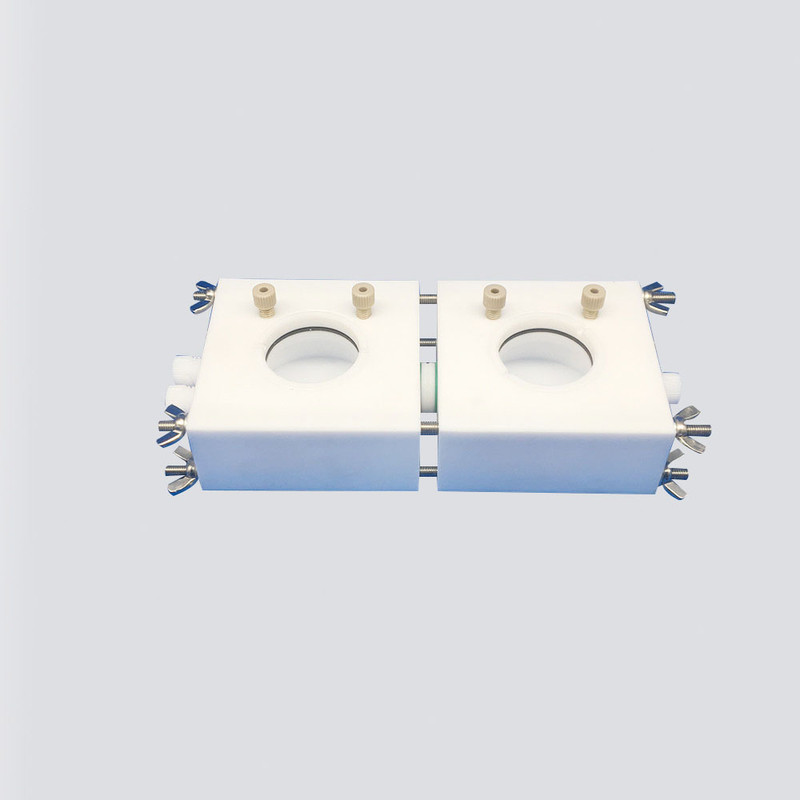
H-type double cell body with double-side light window type is an in-situ Raman characterization cell in which the working electrode and the counter electrode are separated in two chambers. It can be used to test the Raman spectroscopy detection of research materials including the CO2RR reaction process.
characteristic:
1.The main body of the in-situ Raman pool is made of polytetrafluoroethylene material, which is made by meticulous crafting.
2.The size of the working electrode chamber and the counter electrode chamber are both 80*80*30mm, the internal electrolyte solution part is a space of φ55*13mm, and the volume is 30ml. The diameter of the intermediate ion membrane exchange channel is 14mm.
3.The Raman cell is equipped with JGS2 quartz plate, the size of the quartz plate is φ41*1mm. The spectral application range of JGS2 optical quartz glass is 220-2500nm.
4.The standard working electrode of the Raman cell is a PEEK platinum sheet electrode holder, which can hold sheet materials such as carbon paper, metal sheet, metal mesh, foamed nickel, and conductive glass. The distance between the material surface and the quartz sheet is about 5mm. There are also detachable L-shaped glassy carbon electrodes or gold disk electrodes instead, which can reduce the distance between the material surface and the quartz plate to 0.5mm.
5.The standard counter electrode of the Raman cell is a platinum wire electrode, and the electrode size is φ0.5*37mm. There are also φ0.5*100mm or φ0.5*230mm platinum wire ring electrodes instead.
6.The standard reference electrode of the Raman cell is an Ag/AgCl reference electrode. There are also saturated calomel electrodes, Hg/HgO electrodes, Hg/Hg2SO4 electrodes and non-mercury Ag+ reference electrodes instead.
7.The working electrode chamber can hold the working electrode and the reference electrode. Two small holes are opened on both sides of the quartz light window, which can be used to pass air in and out or transport circulating electrolyte. The counter electrode is placed on the side of the counter electrode chamber, and two small holes are opened on both sides of the quartz light window, which can be used to pass air in and out or transport circulating electrolyte.
8.The Raman cell can be quickly assembled and disassembled, and it is easy to clean.
NOTICE:DekResearch's in-situ Raman spectroscopy electrochemical cell is basically suitable for various types of optical microscopes and Raman spectrometers in the world. When the focus distance of the instrument is different, please be sure to contact our technical team in advance

Comments
Post a Comment